According to the adiabatic equation The pressure of the surroundings c.
Equation For Work Done On A Gas. So, h = 2.3026 (rt/j) log10 (v2/v1) since p1v1 = p2v2, thus, v2/v1= p1/p2. This gives us our general method of finding work.
 From venturebeat.com
From venturebeat.com
For the expansion from state 2 to state 3, which is not at constant pressure, the work is still equal to the area under the curve defining the process. This gives us our general method of finding work. For a reversible process in a closed system (no mass entering or leaving), the general equation for the expansion work done by a real gas on the surroundings is the same for an ideal gas, namely.
Denote cp/cv = k, the ratio of specific heat capacities of the gas. When work is done on the gas, the volume of the gas decreases () and work is positive. Pv ϒ = constant (c) hence, substituting this value, we get. Expands from state 1 to state 2, equation 15.2 tells us that the work done by the gas in that process is.
 Source: venturebeat.com
Source: venturebeat.com
When the gas does work the volume of a gas increases () and the work done is negative. The units in which work is expressed will depend on the units of p and v. The work done w by an expanding gas is calculated using w = pδv. When work is done on the gas, the volume of the gas.
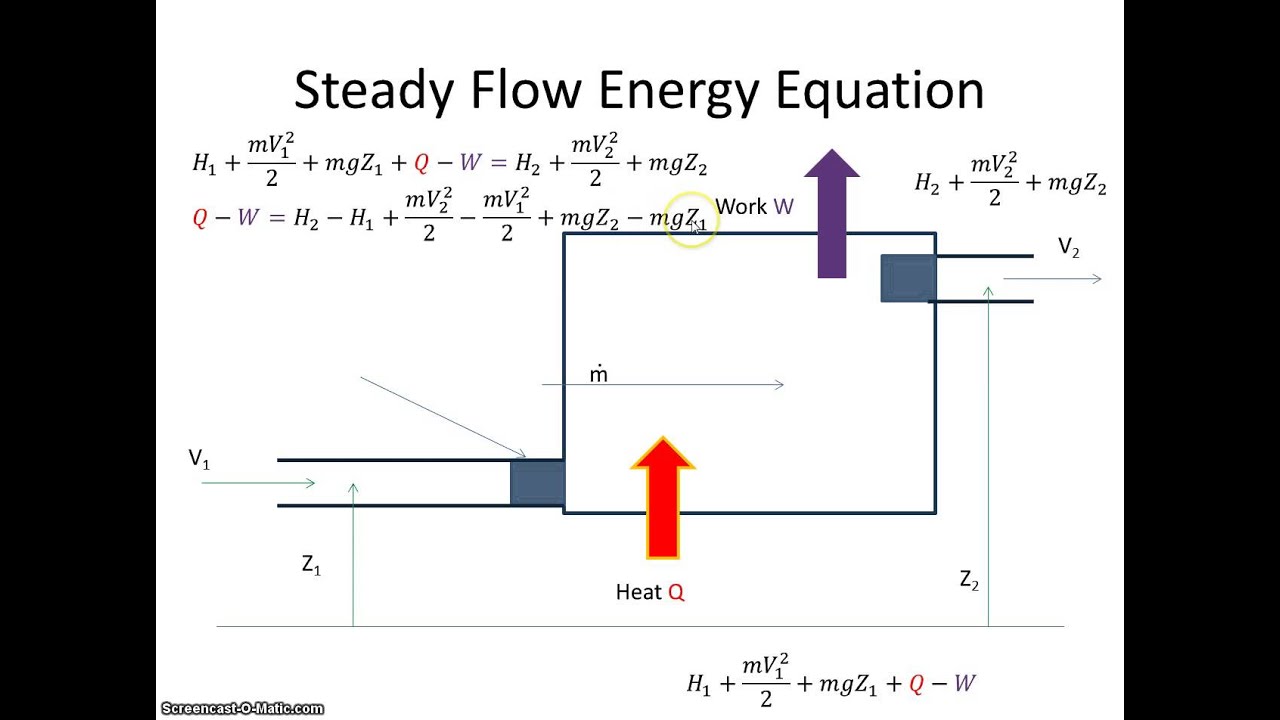 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The work done w by an expanding gas is calculated using w = pδv. This is the area under the curve defining the process. However, for a real gas, we use the equation of state for that gas p = p ( n, v, t) rather than p = n r t v, the equation of state for the ideal.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
As the gas expands adiabatically, there will be a change in p, v, and t from its initial stage (p1, vi, t1) to (p2, vf, t2) total work done will be: If the system does work, the energy comes from heat flowing into the system from the reservoir; For a reversible process in a closed system (no mass entering or.
 Source: venturebeat.com
Source: venturebeat.com
A real gas obeys the equation p (v m − b) =rt, where (b=0.1 l/mol) if 2 moles gas is slowly compressed from 1.2 litre to 0.6 litre at 300 k, then work done in the process is a 1.99 kj As the gas expands adiabatically, there will be a change in p, v, and t from its initial stage.
 Source: slideserve.com
Source: slideserve.com
This gives us our general method of finding work. A real gas obeys the equation p (v m − b) =rt, where (b=0.1 l/mol) if 2 moles gas is slowly compressed from 1.2 litre to 0.6 litre at 300 k, then work done in the process is a 1.99 kj The mathematical representation of the adiabatic process is δq=0. The.
 Source: venturebeat.com
Source: venturebeat.com
For an ideal gas, an adiabatic process is a reversible process with constant entropy. (a) and (b) are correct homework equations w = pδv the attempt at a solution The pressure of the expanding gas b. What must remain constant for this equation to be used? The mathematical representation of the adiabatic process is δq=0.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Expands from state 1 to state 2, equation 15.2 tells us that the work done by the gas in that process is. I am given the volume, pressure and temperature. If work is done on the system, heat flows out of the system to the reservoir. W = −1.10atm × (2.50l− 3.00l) = −1.10atm × −0.50l. According to the adiabatic.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
What must remain constant for this equation to be used? W = ∫ p d v. W= vf ∫ vi pdv. One way to remember the sign convention is to always think about the change in energy from the point of view of the gas. It contains the study of each process to find the work done, heat transfer, and.





